Understanding Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH): Causes, Symptoms & Expert Care by Dr. Apratim Chatterjee
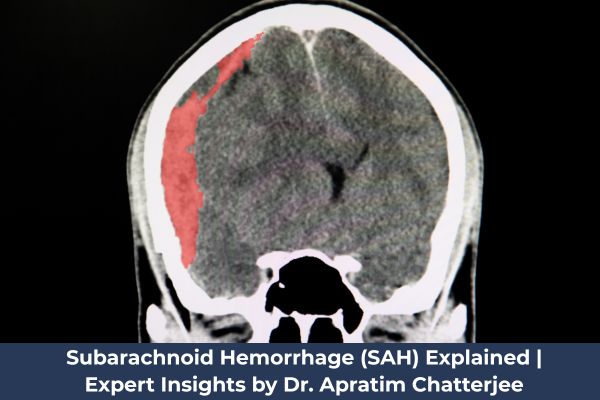
A Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) is a medical emergency caused by bleeding into the space surrounding the brain. This condition can be life-threatening and requires immediate attention. With the advancements in neurocritical care and the expertise of specialists like Dr. Apratim Chatterjee, timely diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve patient outcomes.
What Is Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH)?
A Subarachnoid Hemorrhage occurs when blood leaks into the subarachnoid space, the area between the brain and surrounding membrane. This sudden bleeding increases pressure on the brain, leading to severe neurological disturbances.
Common Causes of SAH
SAH can result from several underlying factors, such as:
1. Ruptured Aneurysm
The most common cause — a weakened blood vessel bursts and causes sudden bleeding.
2. Head Injury
Trauma can result in bleeding around the brain.
3. Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs)
Abnormally connected arteries and veins can rupture.
4. Blood-Thinning Medications or Disorders
Issues with clotting may increase the risk.
Symptoms of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
SAH typically presents with very sudden and intense symptoms, including:
Thunderclap headache (worst headache of life)
Nausea and vomiting
Stiff neck
Blurred or double vision
Loss of consciousness
Seizures
Sensitivity to light
Confusion or difficulty speaking
Recognizing these symptoms early and seeking immediate medical help is crucial.
Diagnosis of SAH
Under the guidance of experts like Dr. Apratim Chatterjee, diagnosis typically includes:
CT Scan (Head)
Lumbar Puncture (if CT is inconclusive)
CTA / MRA (to locate aneurysm or AVM)
Cerebral Angiography
Treatment Options
The treatment approach depends on the cause and severity of bleeding:
1. Aneurysm Clipping
A neurosurgical procedure to stop further bleeding.
2. Endovascular Coiling
A minimally invasive method using coils to seal the aneurysm.
3. Medication
To control blood pressure, prevent vasospasm, and manage pain.
4. Intensive Neurocritical Care
Continuous monitoring in an ICU setting to prevent complications like re-bleeding or stroke.
Role of Dr. Apratim Chatterjee in SAH Management
Dr. Apratim Chatterjee is known for his expertise in diagnosing and treating neurological emergencies, including Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. His approach typically includes:
Quick and accurate diagnosis
Personalized treatment planning
Coordination with neurosurgical teams
Focus on neurocritical care and rehabilitation
Compassionate communication with patients and families
Early treatment under an experienced neurologist significantly improves survival and long-term recovery.
Preventive Measures
While not all SAH cases are preventable, certain lifestyle modifications can reduce risks:
Quit smoking
Control hypertension
Avoid excessive alcohol intake
Manage cholesterol levels
Regular health check-ups
Screen for aneurysms if family history exists
Conclusion
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage is a serious condition requiring rapid and specialized medical care. With prompt treatment, advanced neuroimaging, and expert clinical judgment from specialists like Dr. Apratim Chatterjee, many patients can recover and return to their normal lives. Early recognition of symptoms and immediate hospitalization can be life-saving.