What is Carotid Stenting?
Carotid Stenting is a minimally invasive procedure used to open narrowed or blocked carotid arteries—the major blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the brain. When these arteries become clogged due to plaque buildup (a condition known as carotid artery stenosis), it significantly increases the risk of stroke.
Carotid stenting involves the insertion of a small mesh tube (stent) into the affected artery via a catheter, which helps restore proper blood flow and prevent stroke. This procedure is a safe and effective alternative to traditional surgery, especially for high-risk patients.
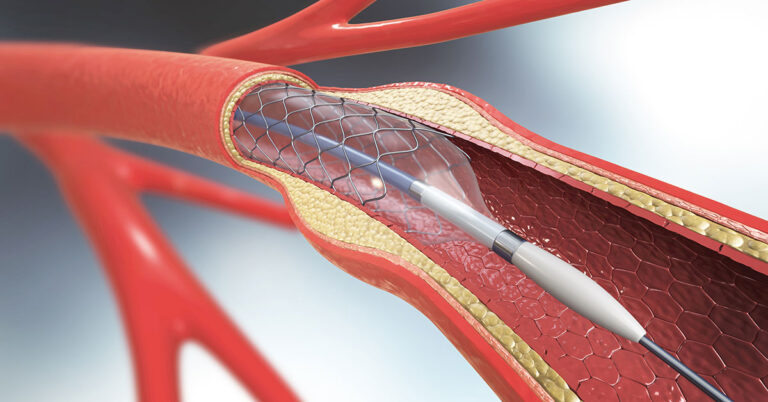
Signs and Symptoms of Carotid Artery Disease
Carotid artery disease may not show symptoms until it becomes severe or results in a stroke or mini-stroke (TIA). Warning signs include:
-
Sudden weakness or numbness in the face, arms, or legs (especially on one side)
-
Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
-
Sudden vision problems in one or both eyes
-
Dizziness or loss of balance
-
Severe headache with no known cause
-
Transient Ischemic Attacks (mini-strokes)
Diagnostic Procedures
Dr. Apratim Chatterjee follows a precise, evidence-based approach to diagnosing carotid artery disease:
Carotid Doppler Ultrasound: A non-invasive test to detect narrowing or blockages
CT Angiography (CTA) or MR Angiography (MRA): Advanced imaging to visualize the arteries and plan the procedure
Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA): The gold standard for detailed assessment before stenting
Neurological Evaluation: To assess brain function and stroke risk Blood Tests & Risk Factor Assessment: To evaluate overall cardiovascular health
Carotid Doppler Ultrasound: A non-invasive test to detect narrowing or blockages
CT Angiography (CTA) or MR Angiography (MRA): Advanced imaging to visualize the arteries and plan the procedure
Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA): The gold standard for detailed assessment before stenting
Neurological Evaluation: To assess brain function and stroke risk Blood Tests & Risk Factor Assessment: To evaluate overall cardiovascular health