Interventional Neurology
Interventional Neurology
Best Interventional Neurology in Kolkata- Dr. Apratim Chatterjee
- Mechanical Thrombectomy
- Cerebral Aneurysm
- Arteriovenous Malformations
- Acute ischemic stroke (AIS)
- Hemorrhagic Stroke
- Carotid Stenosis
- Brain Stroke
It is a type of minimally invasive procedure in which an interventional neuroradiologist removes the clot using special equipment. The doctor makes a very tiny hole or an incision in the groin or the wrist to access the blocked vessel.
Benefits
The effect of the procedure is almost immediate. In some cases, the patient even becomes mobile again or starts speaking immediately. However, other patients may take weeks to months to improve.
A cerebral aneurysm or a brain aneurysm is a balloon-like swelling in your brain’s blood vessels. It typically forms at a weak spot where the arterial wall bulges and fills with blood.
Cerebral Aneurysm Treatment
Management of cerebral aneurysm include:
Observation
In some cases, the ideal treatment is to wait and watch. The doctor will ask you to control high blood pressure and quit smoking. Small(generally less than 3mm), asymptomatic, and unruptured aneurysms can be monitored with scans every year. If the aneurysms show a change in size or shape then they need to be treated.
Surgical Clipping
This procedure involves a cut in the skull under general anesthesia. The brain is retracted, and a small clip is placed on the neck of the aneurysm to prevent blood from entering it. The clip is made up of titanium and stays permanently in the brain.
Recovery time is usually between four to six weeks but may take longer.
Endovascular Coiling
It is a minimally invasive option and is performed during an angiogram. During this procedure, a catheter is introduced in the leg artery through a small cut in the groin, which is then passed to the aneurysm in the brain.
The doctor packs the aneurysm with platinum coils introduced through the catheter. These coils promote clotting, sealing the aneurysm, and preventing blood from entering it. Sometimes in addition to the coils balloon or stent assistance is required.
It may take up to two to four days for complete recovery. Coiling requires periodical monitoring through imaging for five years.
Endovascular flow diversion
When coiling and clipping are difficult due to the size or shape of the aneurysm, flow diversion can come in handy. A flow-diverter stent is a tightly woven mesh tube and is inserted in the main artery across the aneurysm.
The tight mesh stent prevents easy blood flow into the aneurysm, and blood flows through the artery predominantly with minimal flow inside the aneurysm. Lack of blood supply will cause the aneurysm to form thrombus/clot and it gradually disappears.
The recovery time is usually two to four days in an unruptured aneurysm.
Artery occlusion and bypass
This procedure is done very infrequently these days. This procedure is recommended when the aneurysm is inaccessible or large, or the blood vessel is damaged. It involves opening the skull and introducing clips to block the aneurysm and artery.
Now the surgeon bypasses the blood flow around the blocked artery by placing a graft. This graft is a small artery, usually taken from your leg, connected both above and below the occluded artery to allow blood flow through the graft.
Usually, it takes four to six weeks to recover, but it may even take longer.
AVM is usually a congenital condition, meaning it is present at birth. Although AVM may develop everywhere in the body, it is commonly seen in the brain and spine, causing headaches and seizures.
Treatment for AVM
Treatment options for AVM include observation, embolization, radiosurgery, and surgery. The ideal treatment depends on the type and location of AVM, age, and physical health.
Observation
If there is no previous history of bleeding (hemorrhage), your doctor may decide to observe the condition and prescribe medicines to lower blood pressure or prevent seizure.
Embolization
It is a minimally invasive procedure involving the insertion of a flexible, thin tube (catheter) through a cut in the groin to deliver obstructive materials like glue into AVM and close the abnormal connection.
The procedure time may vary for different cases, and the patient has to stay under observation in a hospital. Embolization is less invasive, reducing the risk of side-effects and promoting faster healing. It can be useful in inoperable or deep AVM.
Some disadvantages of the treatment include rebleeding and the risk of embolic stroke. Besides, multiple treatments may be needed.
Radiosurgery
It uses a highly concentrated radiation beam that focuses on the site of AVM. The radiation beam damages the blood vessels and forms a scar tissue that stops the blood flow into the AVM. The patient can go home on the same day. Usually, the AVM blood vessels close after six months to 2 years and are replaced with scar tissue. The procedure is cut-free and painless. Radiosurgery is ideal for smaller AVMs and may take longer to show results.
Conventional Surgery
It involves creating a surgical opening in the skull through which the AVM is cut from the normal brain tissue or shrunken. Various techniques, such as electrocautery and laser, are used for the same.
The patient may need to stay in the hospital between 5 to 7 days. The primary benefit of the procedure is immediate relief from the AVM.
Acute ischemic stroke (AIS) is a sudden loss of blood flow to an area of the brain associated with the loss of neurological functions. Thrombosis or embolism obstructs a blood vessel supplying a specific part of the brain.
Acute Ischemic Stroke Causes
The leading cause of AIS is blockage of the artery supplying your brain with a plaque (fatty buildup) or clot.
Acute Ischemic Stroke Imaging and Intervention
The following tests aids in stroke imaging:
- Computed tomography scan
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- CT or MR angiography
- Cerebral Angiography(DSA)
Acute Ischemic Stroke Management
Acute ischemic stroke treatment mainly consists of the following therapies.
Clot buster drugs (Can be given till 4.5 hrs after stroke onset)
Clot-buster or thrombolytic medicines restore blood flow by dissolving the clot. The most common drug used for this purpose is tissue plasminogen activator or tPA. tPA is an enzyme found in your body and dissolve clots. Your doctor may inject tPA in your blood to speed up the process.
Individuals receiving tPA within the first three to four hours of stroke are more likely to recover faster with little or no disability.
Mechanical Thrombectomy(Can be given till 24 hrs of stroke onset)
Large blood clots that block large arteries may not dissolve fast enough with tPA. In such cases, a minimally invasive procedure, which uses clot retrieval devices to pull out the clot, leaving the artery open, is recommended.
This procedure is done during an angiogram, where a catheter is introduced in a blood vessel through a small hole in the groin. It is called Mechanical Thrombectomy.
Strokes can be of two types. An ischemic stroke results due to a lack of blood flow to the brain cells and tissues. Blockage of brain blood vessels due to clot is major cause of this stroke. Clot can arise from the heart or from the brain blood vessels. An ischemic stroke is the most typical type of stroke and accounts for 87% of stroke cases.Another type of stroke is a hemorrhagic stroke resulting from a ruptured blood vessel in the brain. The blood from the ruptured vessels accumulates and puts pressure on the surrounding brain areas and it can be fatal. Infact, only two-third of the patients of hemorrhagic stroke survive. A hemorrhagic stroke accounts for the remaining 13% of stroke cases and has a higher death rate than ischemic stroke.
Treatment for Hemorrhagic Stroke due to Brain Aneurysms
Medical Management
Once the bleeding is there in the brain, patients become very sick and require early hospital admission preferably in a dedicated neuro ICU. Here, medical management is given to decrease the symptoms of bleeding, manage increased blood pressure and in some cases ventilation if the patient has had severe bleeding. In addition to this, the cause of bleeding the aneurysm needs to be treated urgently because there is a very high chance of repeat bleeding.
Your physician may decide the best hemorrhagic stroke treatment based on the condition. Some common options include:
Endovascular Repair/coiling
In this form of treatment, the neurointerventional surgeon threads a catheter and thin wire through blood vessels into the aneurysm. A coil of platinum wire, which is as thick as a strand of your hair, is released into the area. The coil acts as a net, preventing blood from flowing into the aneurysm. Multiple coils are introduced inside the aneurysm till the time no blood flow is seen inside the aneurysm.
The procedure prevents rebleeding. In this type of treatment, there is no scar over the head and the entire treatment is done through a tiny hole in the groin or wrist. In general, this form of treatment is less risky then open surgery and recovery time is less.
Open Surgery/Clipping
In this form of treatment, the skull is opened up and the brain is separated to reach the site of the aneurysm. Once there the blood flow into the aneurysm is blocked with an aneurysmal clip that prevents it from bursting or bleeding further. Depending on the aneurysm’s size and location, surgery may or may not be a good option.
Coiling Versus Clipping
Both are established treatments for aneurysm treatment. The decision of which modality is better in a given case is based on, location of the aneurysm, size and configuration of the aneurysm, age, existing medical conditions and available local expertise. However, in general, coiling is safer when compared to open surgery in the majority of cases.
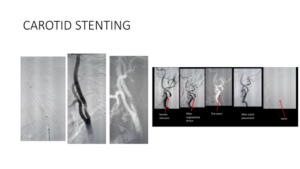
Carotid stenosis is a condition characterized by progressive narrowing of a segment of the carotid artery due to atherosclerosis. A healthy artery is flexible and has smooth walls. However, as you age, small injuries and hypertension may result in a build-up of plaque, a sticky substance made up of cholesterol, calcium, fat, and other fibrous materials. Gradually, plaque deposits and form a large mass, blocking the inside of your blood vessel. Atherosclerosis also causes the arteries to become hard and rigid, resulting in stenosis.
Carotid Stenosis Treatment
Medicines
Patients with low-grade stenosis, typically less than 650%, are treated with medicines.
Some commonly used medicines include:
- Statins or cholesterol-lowering medicines
- Antiplatelet medicines such as aspirin and clopidogrel
- Antihypertensive medications such as ACE inhibitors and angiotensin blockers
Surgery
It is usually recommended for patients with more than one TIAs or who have a moderate- or high-grade stenosis, above 60%.
Some common procedures include:
- Carotid angioplasty/stenting: It is a minimally invasive endovascular procedure performed during an angiogram. A flexible catheter is inserted through a small incision in the groin through the femoral artery to reach the carotid artery. A small catheter with a balloon is placed across the plaque. The balloon is inflated to compress the plaque and dilate the artery. After this, the balloon is deflated and removed. A stent is placed over the plaque, holding open the artery.
- Carotid endarterectomy: It is open surgery to remove the plaque. It requires a cut to be made in the neck, to open the artery and remove the plaque.
Types of Stroke
There are two main types of stroke:
- Ischemic stroke: It results due to reduced blood flow to the brain cells and tissues. Blockage of brain blood vessels due to clot is the major cause. Clot can arise from the heart or the brain blood vessels. An ischemic stroke is the most typical type of stroke and accounts for 87% of stroke cases.
- Hemorrhagic stroke: It results from a ruptured blood vessel in the brain. The blood from the ruptured vessels accumulates and puts pressure on the surrounding brain areas, and it can be fatal. In fact, only two-third of the patients with hemorrhagic stroke survive. A hemorrhagic stroke accounts for the remaining 13% of stroke cases and has a higher death rate than ischemic stroke.
Brain Stroke Treatment
The doctor will decide the ideal treatment based on the type of stroke, causes, and stroke onset.
Ischemic Stroke
- Clot buster drugs (Can be given till 4.5 hours after stroke onset)
- Mechanical Thrombectomy (Can be done till 24 hours of stroke onset)
Procedures such as carotid endarterectomy and angioplasty and stents can also help manage ischemic stroke.
Hemorrhagic Stroke
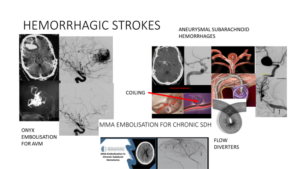
- Emergency measures: This includes medicines to lower blood pressure and neutralize the effect of blood thinners.
- Surgical clipping: A tiny clamp is used at the base of the aneurysm to stop blood flow to it.
- Coiling: Here, tiny detachable coils are placed into the aneurysm to fill it to block blood flow into the aneurysm.
- Surgical removal of AVM: Smaller AVMs present in accessible brain area are removed surgically, eliminating the risk of rupture.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery: It is an advanced minimally invasive treatment. Here, multiple beams of highly focused radiation are used to repair blood vessel malformations.
Book An Appointment Today
With Best Interventional Neurologist in Kolkata Dr. Apratim Chatterjee Today!
Call Now Visit Dr. Chatterjee
